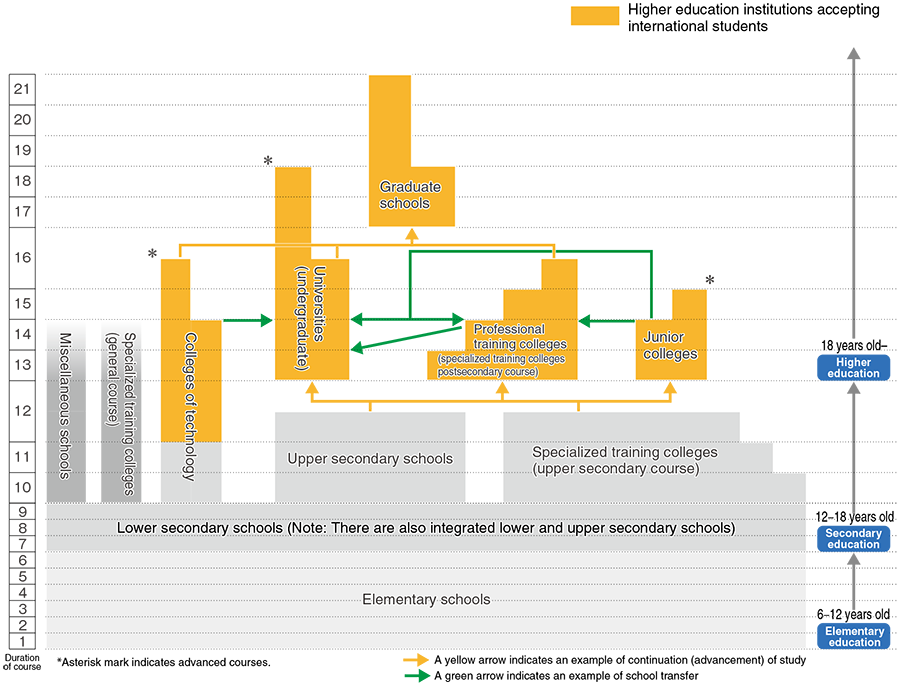
Higher Education In Japan
Higher education in Japan begins after the completion of 12 years of schooling. The Japanese education system follows a basic of 6-3-3-4 pattern. There are five types of higher education institutions that international students can enter. They are divided into national, local public and private according to their administration.
In general, the academic year in higher education institutions in Japan begins in April and ends in March of the following year.
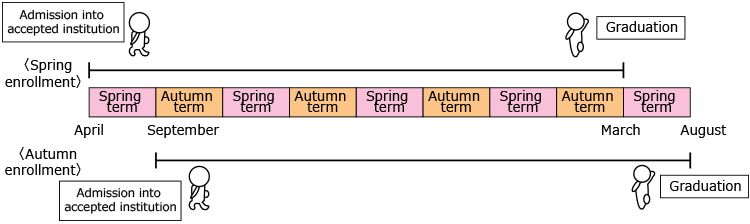
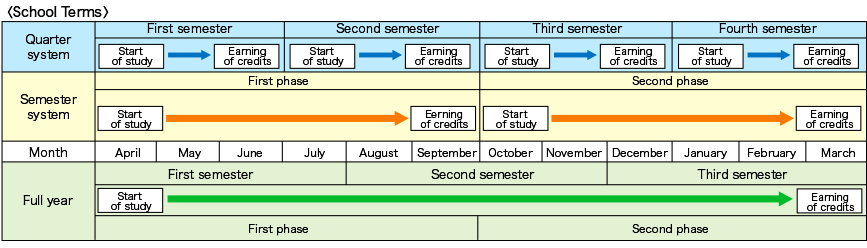
First semester begins in April and ends in September. Second semester begins in October and ends in March of the following year. Vacations vary according to universities and departments. Summer : late July ~ early September. Winter : late December ~ early January. Spring : February ~ March.
STPM, A-Level, UEC, IBD, Diploma or equivalent qualifications (12 years of formal education) are required for entrance into Japanese higher education institutions.
For SPM, IGCSE/GCE O-Level qualifications (without 12 years of formal education), complete a year of “University Preparatory Course” (or Pre-U as it is better known in Malaysia), at one of the designated Japanese language institutes by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) is necessary. In general, proficiency in Japanese language is prerequisite for entrance into Japanese higher education institutions, except for the undergraduate and postgraduate courses which are offered in English language.
